Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), includes Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). The exact etiology and pathogenesis of IBD have not been fully acknowledged.
Recent studies have investigated the relationship between gut microbiota and IBD.
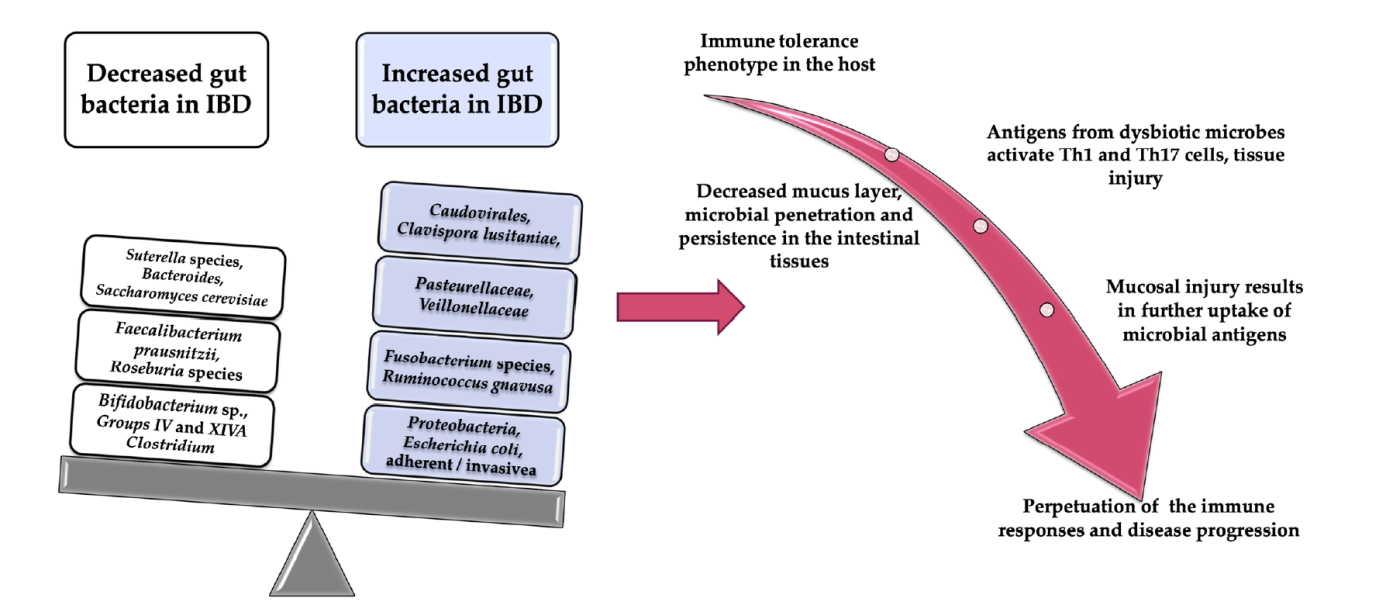
Dysbiosis is an important factor in the intestinal inflammation. Thus, gut microbiome management is likely to be an objective in IBD treatment.
probiotics
The existing evidence suggests the beneficial role of probiotics in the treatment of IBD. Mechanisms of action that researchers have suggested for probiotic include: stimulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines production, antimicrobial substances secretion, suppression of bacterial growths, modulation of immune system, immunomodulatory role, improvement of the epithelial barrier function, and suppression of T-cells proliferation.
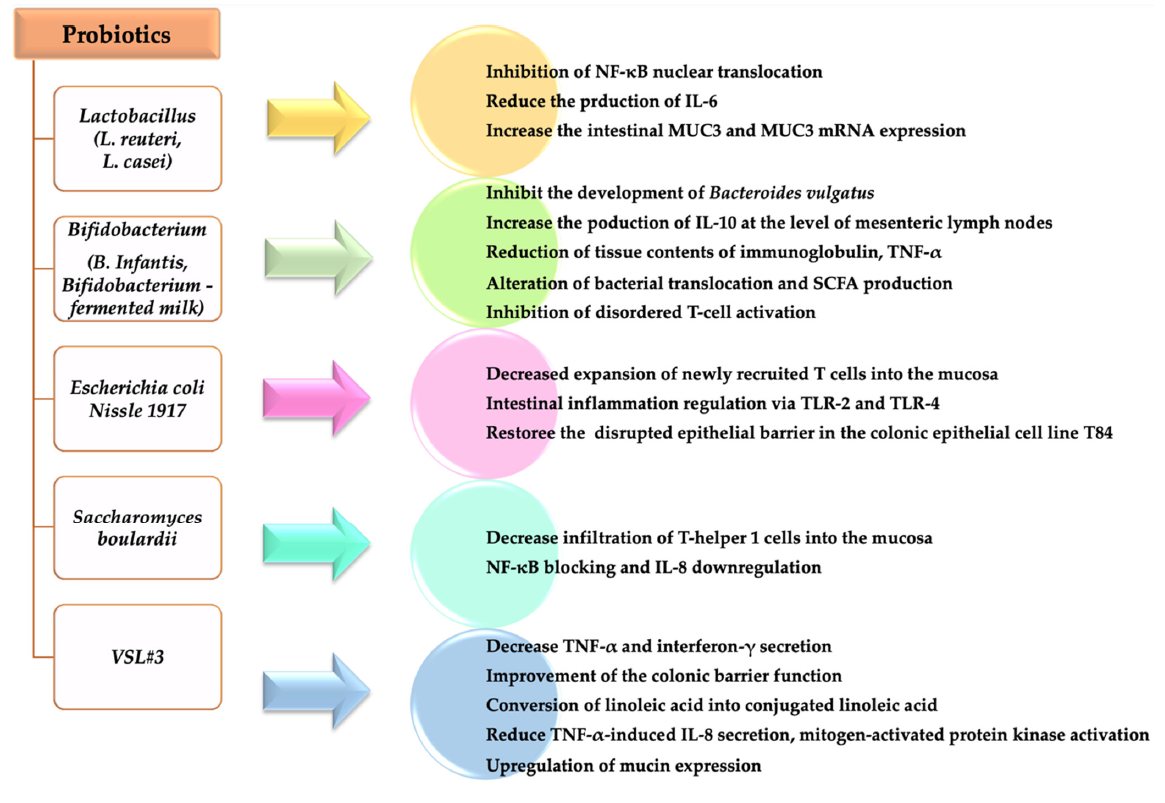
The effectiveness of probiotic agents in maintaining the clinical remission of the Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis have been shown in several studies.
prebiotics
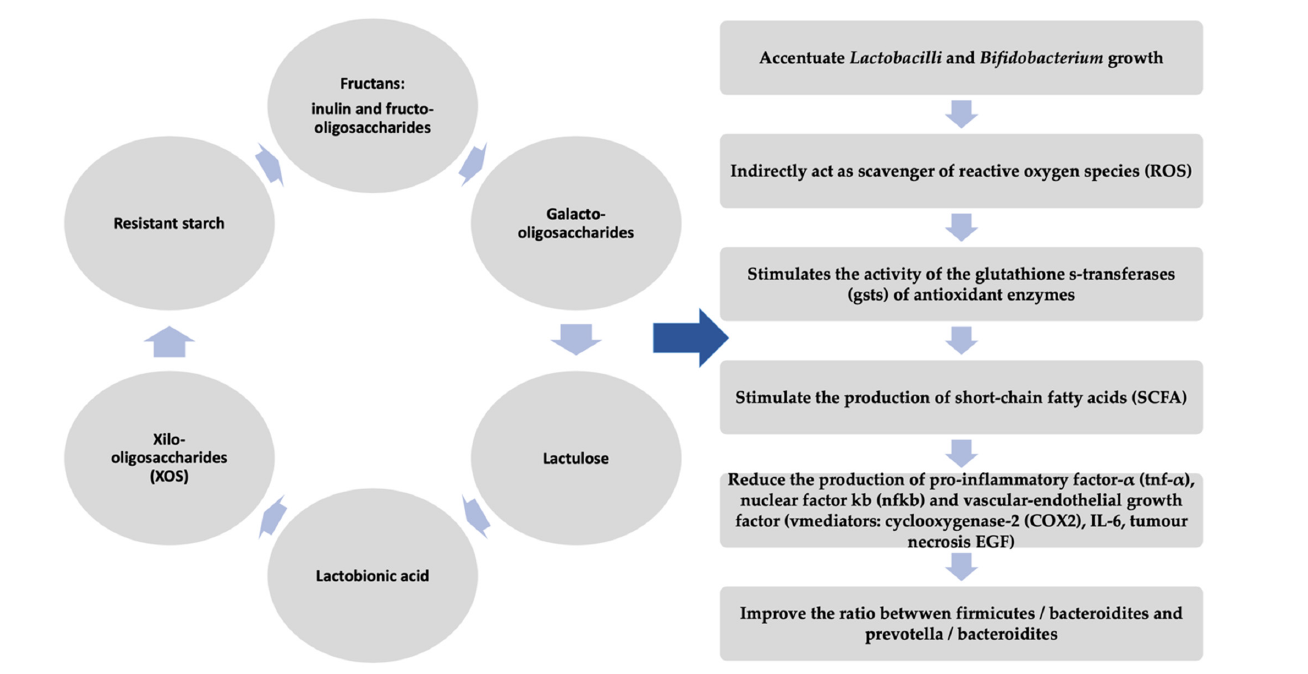
prebiotics are functional non-digestible food components include fructo-oligosaccharides, inulin, and galacto-oligosaccharides. prebiotics stimulate the activity or the growth of some specific groups of bacteria, e.g. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus and the bacterial production of short chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, with immunoregulatory effects.
Fecal Microbiota Transplant (FMT)
FMT can lead to increasing the production of short-chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, improving the integrity of the intestinal barrier and thus reducing bowel permeability and severity of IBD.
Natural Chemical Compounds in IBD Treatment
Health benefits of phytochemicals have been reported by several studies. The gut microbiota and immunity of the intestine has been reported to be influenced by a number of polyphenols, such as flavonoids, phenolic acids and lignans, which have numerous biological benefits (antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory). A significant involvement of polyphenols in CD and UC has been reported by recent epidemiological study.
Conclusion
Recently, the importance of intestinal microbiota in maintaining the normal functioning of the body has been more and more recognized. Recent evidence suggested the relationship between dysbiosis of intestinal microbiota and IBD. An approach based on the intestinal microbiota for the treatment of IBD developed in recent years.
Probiotics have been shown to promote gut health, modulate the immune system and reduce the risk of IBD among high-risk patients.
The health benefits of probiotic agents, especially those of the Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, were reported in UC and CD. The mechanisms behind these results are the immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of probiotic agents. In other words, probiotics reduce the synthesis of pro-inflammatory mediators and increase the synthesis of anti-inflammatory mediators.
References:
Pavel FM, Vesa CM, Gheorghe G, Diaconu CC, Stoicescu M, Munteanu MA, Babes EE, Tit DM, Toma MM, Bungau S. Highlighting the Relevance of Gut Microbiota Manipulation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Jun 15;11(6):1090. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11061090.

