The use of antibiotics to fight microbial infections is a cornerstone of modern medicine. However, antibiotics can also disrupt the delicate balance of our gut microbiome, leading to side effects like antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and potentially contributing to antibiotic resistance. This is where probiotics come in, raising the question: can co-prescribing antibiotics with probiotics be an efficient strategy?
The Potential Benefits:
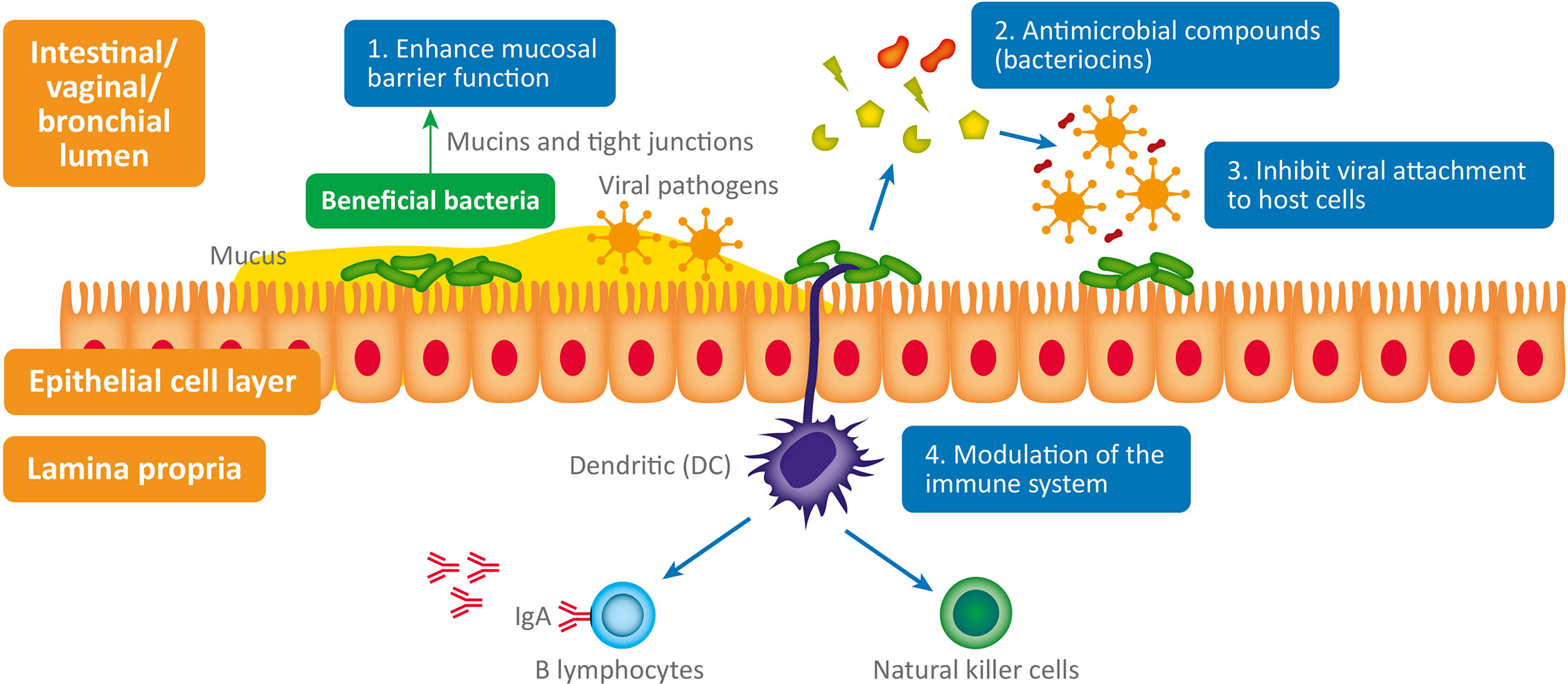
Reduced AAD: Studies suggest probiotics can help prevent AAD, a common side effect affecting up to 30% of antibiotic users. They may achieve this by:
Competing with harmful bacteria: Probiotics occupy space and resources, hindering the growth of pathogens.
Boosting immune function: Probiotics can stimulate the immune system to fight off infections more effectively.
Restoring gut barrier function: Probiotics may help maintain the integrity of the gut lining, reducing inflammation and preventing the invasion of harmful bacteria.
Improved treatment outcomes: Some studies suggest co-prescribing probiotics might enhance the effectiveness of antibiotics against certain infections. This may be due to their ability to modulate the gut microbiome, creating an environment less favorable for pathogens.
Reduced risk of antibiotic resistance: By promoting a healthy gut microbiome, probiotics may indirectly reduce the selection pressure for antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
However, the picture is not entirely clear:
Limited evidence: While promising, the research on coprescribing antibiotics with probiotics is still evolving. More high-quality studies are needed to confirm the benefits and identify the most effective probiotic strains for specific infections.
Strain specificity: Different probiotic strains have varying effects. Choosing the right strain for the specific infection and individual patient is crucial for optimal results.
Timing and dosage: The timing and dosage of both antibiotics and probiotics are critical for their effectiveness. Further research is needed to determine the optimal regimen.
Safety concerns: While generally safe, there are potential risks associated with probiotics, especially in immunocompromised individuals. Consulting a healthcare professional before using probiotics is essential.
Conclusion
Overall, co-prescribing antibiotics with probiotics holds promise for managing microbial infections while minimizing side effects. However, more research is needed to optimize this approach and ensure its safety and efficacy for various infections and patient populations. Always consult your doctor before starting any new treatment, including probiotics.
Provided by: Dr. Babak Tamizifar