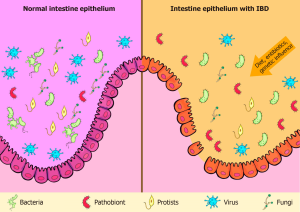
The human intestine is colonized by 10–۱۰۰ trillion commensal bacteria that are involved in the digestion process, modulation of immune response, and other functions. Nowadays, due to excessive use of antibiotics, stress conditions, and hygiene, we encounter gut dysbiosis.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are defined as a “substrate that is selectively utilized by host microorganisms conferring a health benefit”.
In order to be categorized as a prebiotic, a product must meet several conditions:
- It should stimulate the proliferation and activity of some beneficial strains of gut bacteria
- It should create a favorable medium to some beneficial bacteria in the colon
- It should be resistant to the action of digestive enzymes and process of hydrolysis
- It should not be absorbable in the upper digestive tract
- It should not be destroyed during the food processing process
- It should decrease the pH in the intestinal lumen
Research data demonstrate that prebiotics determine the change of gut microbiota spectrum and bacteria metabolites. However, there are still few data published regarding prebiotics in IBD. To date, results of prebiotic research in patients with IBD are conflicting. Although the administration of prebiotic agents may be associated with some adverse digestive side effects in active IBD, their administration in early childhood for a proper development of gut microbiome and later prevention of IBD onset should be taken into consideration.
Probiotics
Probiotics are live organisms that are beneficial for the gut by modulating the immune response, increase the IgA production and enhance the host immune system`s defenses. Also, they are able to compete with pathogens.
The favorable actions of probiotics on human gut are the following:
- Change of intestinal pH
- The production of components with antibacterial activity (e.g., lactic acid, bacteriocins, hydroperoxides)
- Competition for essential nutrients
- Competitively block the binding sites on the epithelial cells and upregulate tight junction molecules of the mucosal barrier
- The degradation of the receptors for toxins
Lactic-acid-producing bacteria (LAB) include the biggest part of gut microbiota, which produce lactic acid as a result to the anaerobic digestion of saccharides. Lactobacillus spp. are the most important group of bacteria found in fermented food (e.g., pickles, soured milk, kefir) and are considered to be beneficial for humans.
In case of IBD patients, there is an abnormal activation of the immune system due to chronic intestinal inflammation. The use of probiotics may help the transition from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state at the gut level. Nowadays, the strains currently available as probiotics are represented by the Bifidobacterium species, Lactobacillus strains, Bacillus species, Enterococcus faecium, Saccharomyces boulardii, and Pediococcus, which have been demonstrated to be associated with the beneficial health effects. Probiotic engineering determines the formation of bacterial strains with more powerful properties to target the enteric pathogens and to specifically intervene in the disease. This strategy uses bacteria or yeasts genetically engineered with the genes for some therapeutic agents that are acting as anti-inflammatory agents.
References:
- Lazăr DC, Moacă EA, Cornianu M, Tăban S, Faur A, Goldiș A. Efficiency of Treatment Targeted on Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Current Strategies and Perspectives.
- Levine A, Rhodes JM, Lindsay JO, Abreu MT, Kamm MA, Gibson PR, et al. Dietary guidance from the International Organization for the Study of inflammatory bowel diseases. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2020;18:1381-1392
- Eindor-Abarbanel A, Healey GR, Jacobson K. Therapeutic advances in gut microbiome modulation in patients with inflammatory bowel disease from pediatrics to adulthood. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021;22:12506
Provided by Dr. Nazila Kassaian